Journal of Andrology & Gynaecology
Download PDF
On the whole out of 100 pts - 54 patients were primipara and 46 were multipara.
Research Article
Comparative Study between New Novel Biomarker Antiphosphatidylserine/prothrombin Antibodies and Conventional Established Diagnostic Markers in the Lab Diagnosis of Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Gupta A*, Bhardwaj S, Nakra R and Lal V
Department of Hematology and Immunology. National Reference Lab, Dr Lal Path Lab, Rohini, New Delhi, India
*Address for Correspondence:Ajay Gupta, Department of Hematology and Immunology, National
Reference Lab, Dr Lal Path Lab, Rohini, New Delhi, India. E-mail Id: ajay.gupta@lalpathlabs.com
Submission:20 March, 2025
Accepted:18 April, 2025
Published:22 April, 2025
Copyright: © 2025 Gupta A, et al. This is an open access article
distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which
permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium,
provided the original work is properly cited.
Keywords:Bad Obstetric History; Antiphosphatidylserine-Prothrombin; Antiphospholipid Syndrome; Lupus Anticoagulant
Abstract
Background:Ant phosphatidylserine/prothrombin complex (aPS/PT) antibodies are emerging as an important marker in the lab diagnosis antiphospholipid syndrome (APS).
We aimed to compare performance of new novel marker aPS/PT antibody with that of conventional antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) such as lupus anticoagulant (LA), anticardiolipin (aCL), and anti-β2-glycoprotein I (anti-β2GPI) in suspected APS patients. In this study we aimed to find the percentage of cases positive for aPS/PT antibodies in cases with bad obstetric history who had one or more antiphospholipid antibody positivity
needed for diagnosis of APS. We further compared IgG and IgM component of aPS/PT with IgG and IgM components of aCL and anti-β2GP 1. Also,Cases which were positive for LA was also tested for aPS/PT to find the correlation.
Methods:Total 100 samples (registered for BOH panel) who fulfilled the lab criteria for diagnosis of APS were included in the study. IgG/IgM aCL, IgG/IgM anti-β2GPI and IgG/IgM aPS/PT were detected in serum using ELISA assay in Quantalyser 3000 (Inova, San Diego, CA, USA). Lupus Anticoagulant was detected using Star Max (Diagnostica Stago, France).The two different coagulation tests used to detect Lupus anticoagulant (LA) were PTT-LA and dRVVT.
Results:Among 100 patients who fulfilled the lab criteria of APS having BOH included in our study showed 65% positivity for aPS/PT IgG/IgM. Both IgG aPS/PT and aPS/PT IgM were seen in 60 cases out of 65. Significant association were found on comparing the presence of aPS/ PT IgG with Cardiolipin IgG and aPS /PT IgM with Cardiolipin IgM ie 85% and 95% respectively Also association was seen on comparing the presence of aPS/ PT IgM with Beta 2 glycoprotein IgM ie. 57% and significant correlation with Beta 2 Glycoprotein IgG ie 85%. Out of 8 cases with LA positive result, 7(87.5%) were positive for aPS/PT, hence showing highly significant association.
Conclusion:aPS/PT antibody is closely associated with conventional antibodies of APS including LA. The determination of aPS/PT in clinical practice, in conjunction with that of other aPL, may improve the likelihood lab diagnosis of APS.
Methods:Total 100 samples (registered for BOH panel) who fulfilled the lab criteria for diagnosis of APS were included in the study. IgG/IgM aCL, IgG/IgM anti-β2GPI and IgG/IgM aPS/PT were detected in serum using ELISA assay in Quantalyser 3000 (Inova, San Diego, CA, USA). Lupus Anticoagulant was detected using Star Max (Diagnostica Stago, France).The two different coagulation tests used to detect Lupus anticoagulant (LA) were PTT-LA and dRVVT.
Results:Among 100 patients who fulfilled the lab criteria of APS having BOH included in our study showed 65% positivity for aPS/PT IgG/IgM. Both IgG aPS/PT and aPS/PT IgM were seen in 60 cases out of 65. Significant association were found on comparing the presence of aPS/ PT IgG with Cardiolipin IgG and aPS /PT IgM with Cardiolipin IgM ie 85% and 95% respectively Also association was seen on comparing the presence of aPS/ PT IgM with Beta 2 glycoprotein IgM ie. 57% and significant correlation with Beta 2 Glycoprotein IgG ie 85%. Out of 8 cases with LA positive result, 7(87.5%) were positive for aPS/PT, hence showing highly significant association.
Conclusion:aPS/PT antibody is closely associated with conventional antibodies of APS including LA. The determination of aPS/PT in clinical practice, in conjunction with that of other aPL, may improve the likelihood lab diagnosis of APS.
Introduction
The antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a systemic autoimmune
disease characterized by thrombosis and/or pregnancy morbidity
in the presence of persistently positive antiphospholipid (aPL)
antibodies. The updated Sydney APS classification criteria include
anticardiolipin antibodies (aCL), anti-β2glycoprotien-I (anti-β2GP-I)
and lupus anticoagulant (LA) as part of the serological criteria [1].
The latest 2023 ACR/EULAR APS classification criteria include
an entry criterion of at least one positive antiphospholipid antibody
(aPL) test within 3years of identification of an aPL-associated
clinical criterion, followed by additive weighted criteria (score range
1–7 points each) clustered into 6 clinical domains (macrovascular
venous thromboembolism, macrovascular arterial thrombosis,
microvascular, obstetric, cardiac valve, and hematologic)and 2
laboratory domains (lupus anticoagulant functional coagulation
assays, and solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for
IgG/IgM anti cardiolipin and/or IgG/IgM anti–β2-glycoprotein I
antibodies). Patients accumulating at least 3 points each from the
clinical and laboratory domains are classified as having APS[2].
aPL antibodies consist of family of other autoantibodies such
as anti-phosphatidylserine/prothrombin (aPS/PT), anti-vimentin,
anti-annexin, anti-phosphatidylethanolamine and antibodies
directed against domain I of the β2GP-I molecule [3]. The inclusion
of aPS/PT testing in the diagnostic workup of APS patients has been
shown to add to the identification of individuals with APS [4]. Also,
testing of aPS/PT testing and combining with other aPL testing,
such as the concomitant positivity for LA, aβ2GPI and aPS/PT tests,
has been reported to be highly associated with the clinical features
of APS patients, particularly vascular thrombosis, and obstetric
complications [5]. Studies have demonstrated that the addition of
aPS/PT improves risk stratification in APS [6].
Materials and Methods
Patient cohort:
The present study was conducted in the Department of
Haematlogy and Immunology, Dr. Lal Pathlabs, NRL over a period
of 6 months.Total 100 samples (registered for BOH panel) which
fulfilled the lab criteria for diagnosis of APS were included in the
study. Age of patients ranged from 22-46 years. 67 patients were of
age group 30-40, 26 of 20-30 age group and 7 patients above 40 years.On the whole out of 100 pts - 54 patients were primipara and 46 were multipara.
Methods
Antibodies to phosphatidylserine-prothrombin (aPS/PT):
The presence of IgG/IgM aPS/PT were detected in serum using
ELISA assay in Quantalyser 3000 (Inova, San Diego, CA, USA). The
cut off values for IgG and IgM aPS/PT is >30 units.Antibodies to cardiolipin (aCL) and β2- glycoprotein I (anti- β2GPI):
IgG/IgM aCL and IgG/IgM anti-β2GPI were detected in serum
using ELISA assay in Quantalyser 3000 (Inova, San Diego, CA, USA).
The cut off for IgG/IgM aCL is >20 GPL/MPL and for IgG/IgM anti-
β2GP1>20 units.Lupus anticoagulant (LAC):
LA was detected using Star Max (Diagnostica Stago, France). The
two different coagulation tests used to detect Lupus anticoagulant
(LA) were PTT-LA using Lupus anticoagulant sensitive APTT
reagent and dilute Russell venom viper time (dRVVT). LA test was
done with series of functional coagulation test. Both screening and
confirming steps were performed. The LAC was considered positive
if the normalized ratio ie. dRVVT screen ratio/ dRVVT confirm ratio
is >1.20.Results
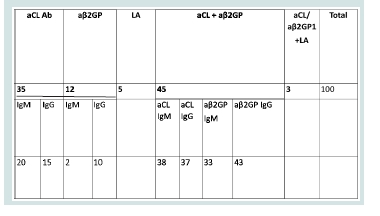
Among these 100 patients with conventional antibodies and
BOH, 65 patients were positive for aPS/PT IgG/IgM. Both IgG and
IgM were seen in 60 cases out of 65.
We separately compared presence of aPS/PT IgG with aCL IgG
and aβ2GP1 IgG and aPS/PT IgM with aCL IgM and aβ2GP1 IgM
aPS/ PT IgG vs Beta glycoprotein1 IgG =85%
aPS/ PT IgM vs Beta glycoprotein1 IgM =57%
aPS/ PT IgG vs Cardiolipin IgG=85%
aPS /PT IgM vs Cardiolipin IgM= 95%
Out of 8 cases with LA positive result 7(87.5%) were positive for
aPS/PT.
Discussion
This study was conducted to find the usefulness of aPS/PT
antibody in the lab diagnosis of APS. We studied the correlation and
percentage positivity of aPS/PT IgG/IgM in patients already having
any 1 or more conventional antibody positivity along with clinical
symptom of bad obstetric history.
aPS/PT have been widely investigated as an additional marker
for APS. In a study conducted in France on the prevalence and
significance of non-conventional Antiphospholipid antibodies in
patients with clinical APS showed a high prevalence of IgG/IgM PS/
PT antibodies. Prevalence of aPS/PT IgM was 65.8% and IgG was
43.9%.Further all patients who were positive for aβ2GP1 IgG were
positive of aPS/PT [7]. In our study 65% positivity of aPS/PT was
seen in patients with one clinical symptom and any 1 conventional
antibodies. 85% patients who were positive for β2GP1 IgG were also
positive for aPS/PT. In a Chinese study to determine the prevalence
and clinical association of aPS/PT with thrombosis and pregnancy
loss showed a positivity of 72% for aPS/PT IgG and 67.2% positivity
for aPS/PT IgM. Both IgG and IgM were present in 53.2% patients [8].
In our study both IgG and IgM aPS/PT was found in 60% patients.
LA detection is important in case of thrombosis recurrence in
patients undergoing treatment. LA detection method is not accurate
for patients who are being treated with DOACs. Patients undergoing
treatment with DOACs could give false positive result with dRVVT
[9].In an article published by American College of Rheumatology
showed most patients who were positive for IgG/IgM anti-PS/PT
antibodies had LAC [10]. In our study out of 8 cases of LA positive
patients 7 had aPS/PT. PS/PT antibodies testing is performed on
serum sample by immunological assays and is not influenced by
treatment of DOACs. Replacing LA testing or using in conjunction
with aPS/PT in patients treated by DOACS need to be considered.
Conclusion
aPS/PT is closely associated with conventional antibodies of
APS and LAC, and positive results from an aPS/PT test can mark
thrombotic events in APS patients.
Further studies can be done to evaluate the use of aPS/PT as surrogate APS biological marker instead of LA to classify in high-risk profile patients treated by direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), in whom LA detection cannot be achieved.
Further studies can be done to evaluate the use of aPS/PT as surrogate APS biological marker instead of LA to classify in high-risk profile patients treated by direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), in whom LA detection cannot be achieved.
The determination of aPS/PT in clinical practice, in conjunction
with that of other aPL, may improve the likelihood of recognizing
APS.