Obesity plays a major public health concern that leads to numerous metabolic, mechanical and psychological complications. Even though lifestyle interventions are the cornerstone of obesity management, following physiological neurohormonal adaptations limit weight loss, strongly favour weight regain and counteract sustained weight loss. A series of effective therapies are needed to manage this chronic relapsing disease.
Bariatric surgery is the mo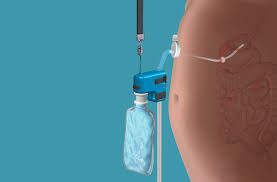 st effective and durable treatment of obesity and its comorbidities, therefore there is a need for less invasive yet efficacious weight loss therapies.Bariatric surgery delivers substantial, durable weight loss but limited access to care, perceived high risks and costs restrict uptake. Medical devices are uniquely situated to bridge the gap between conservative lifestyle intervention and weight-loss pharmacotherapy and more disruptive bariatric surgery. The range of gastrointestinal medical devices that are accessible in clinical practice to treat obesity, as well as those that are in advanced stages of development. It focus on the mechanisms of action as well as the efficacy and safety profiles of these devices. Most of these devices are placed endoscopically, which provides gastroenterologists with exciting opportunities for treatment.
st effective and durable treatment of obesity and its comorbidities, therefore there is a need for less invasive yet efficacious weight loss therapies.Bariatric surgery delivers substantial, durable weight loss but limited access to care, perceived high risks and costs restrict uptake. Medical devices are uniquely situated to bridge the gap between conservative lifestyle intervention and weight-loss pharmacotherapy and more disruptive bariatric surgery. The range of gastrointestinal medical devices that are accessible in clinical practice to treat obesity, as well as those that are in advanced stages of development. It focus on the mechanisms of action as well as the efficacy and safety profiles of these devices. Most of these devices are placed endoscopically, which provides gastroenterologists with exciting opportunities for treatment.
Treatment Devices for Obesity:
Treatments ranges from healthy eating and exercise, to prescription medicine and surgery. FDA-regulated medical devices also helps to treat obesity. Currently, there are four types of FDA-approved devices are designed to treat obesity:
- Gastric Band which are placed around the top portion of the stomach which leaves a small portion available for food.
- Electrical Stimulation Systems is a electrical stimulator that is placed in the abdomen to block nerve activity between the brain and stomach.
- Gastric Balloon Systems are inflatable balloons that are placed in the stomach to take up space.
- Gastric Emptying Systems is a tube and it is inserted between the stomach and outside of abdomen to drain food after eating.
Currently the Food and Drug Administration approved two endoscopically placed intragastric balloon devices and a surgically placed vagal blockade device. Another device that holds particularly for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, which is the endoscopically placed duodenojejunal bypass sleeve.
