Prenatal screening is a subfield of gynecology and clinical genetics. Prenatal diagnosis is the ability to identify the abnormalities in the fetus before birth. The main aim of prenatal diagnosis is to distinguish abnormalities in fetal life and to allow termination. The goals for prenatal screening are to provide a range of informed choice to the couples at risk of having a child with an abnormality, to reduce anxiety and to provide reassurance, particularly among high-risk groups. It is also used to detect the high risk to identify the presence or absence of the disorder by testing. It provides appropriate management like psychological, pregnancy/delivery, and also to enable prenatal treatment for the affected foetus.
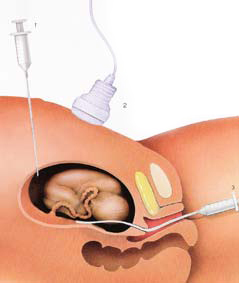 Advanced maternal age is the common indication for prenatal diagnosis. The indications are chromosome abnormality in previous child, gene disorders, neural tube defect and abnormalities identified in pregnancy.
Advanced maternal age is the common indication for prenatal diagnosis. The indications are chromosome abnormality in previous child, gene disorders, neural tube defect and abnormalities identified in pregnancy.
The benefits of prenatal screening are malformation incompatiblility with life can be terminated and certain abnormalities can be corrected in-utero.
The disorders of prenatal diagnosis are classified in to congenital abnormalities are chromosomal, structural abnormalities and genetic and non-genetic disorders. The methods for detecting prenatal diagnosis are Cordocentesis, Preimplatation genetic diagnosis, maternal serum estriol, maternal serum beta -HCG and non-invasive techniques like ultrasonography, invasive techniques like Amniocentesis, Chorionic villus sampling, fetal blood sampling, Fetoscopy and embryoscopy. The molecular techniques are Fluorescent insitu hybridization southern blotting, Polymerase chain reaction.
The risks of prenatal diagnosis and screening are pregnancy complications, pregnancy loss and parental anxiety. The problems in prenatal screening are culture failure, ambiguous chromosome result. Biochemical markers of prenatal diagnosis are Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), Inhibin-A.
The pros of prenatal screening are problems can be corrected before the birth of the baby whereas cons are psychological pressure and expensive. Advances in the fields of maternal-fetal medicine, radiology, and genetics have greatly improved prenatal diagnosis.
